Expanding into new markets is exciting, but choosing the right business expansion strategy can be overwhelming. This guide will explore market entry strategy to help you choose the best fit for your business goals and resources.
What is a market entry strategy?
Conducting a market entry strategy is crucial to ensuring the success of a business aiming for new market penetration.
A market entry strategy is designed to increase a product’s or service’s visibility and distribution in a new market.
Market entry research is crucial for brands aiming to expand into unfamiliar domestic or international markets, where competitive, legal, political, or cultural factors might be less understood.
Market entry research serves as a gateway to comprehending a new market. It aids brands in identifying key success factors, uncovering potential obstacles, and discovering hidden opportunities.
Understanding the market entry strategy approach
There’s no one-size-fits-all approach when it comes to market entry. Choosing the proper strategy relies on several aspects, including:
- Market: Who are you trying to reach? Understanding their needs, preferences, and buying behaviors is crucial.
- Industry: Are you entering a well-established market or a new frontier?
- Resources: What budget and team size do you have available?
- Competition: Who are your current or potential competitors?
3 things to consider before entering a new market
Expanding into new markets is challenging and costly, but what reasons justify this investment? Here are some of the primary motivations:
1. Expand your customer base and increase profitability
The main reason to explore new markets is to grow your business and boost earnings by selling more products to a broader range of customers.
2. Exhausted growth potential in your domestic market
If your local market has reached its revenue limits, venturing into new markets may be the sole path to further expansion.
3. Diversify business risks
By entering multiple markets, you can spread risks. If one market encounters difficulties, others can provide stability and support to sustain your business operations.
Choosing the best market entry strategy
The “best” market entry strategy is the one that best aligns with your specific goals, resources, and market conditions.
Perform comprehensive market research, evaluate competitor strategies through competitive analysis, and seek professional advice to determine the most suitable approach.
Before entering a new market, it’s crucial to consider several factors:
- Regulatory environment: Understand the legal and regulatory landscape clearly to ensure compliance.
- Cultural differences: Show sensitivity to cultural nuances and adapt accordingly.
- Logistics and infrastructure: Consider the logistics of distribution, supply chain management, and infrastructure.
- Financial considerations: Factor in currency fluctuations, potential tariffs, and other financial implications.
Read more: Guide to obtaining a business registration number in Indonesia
9 types of market entry strategy for international markets
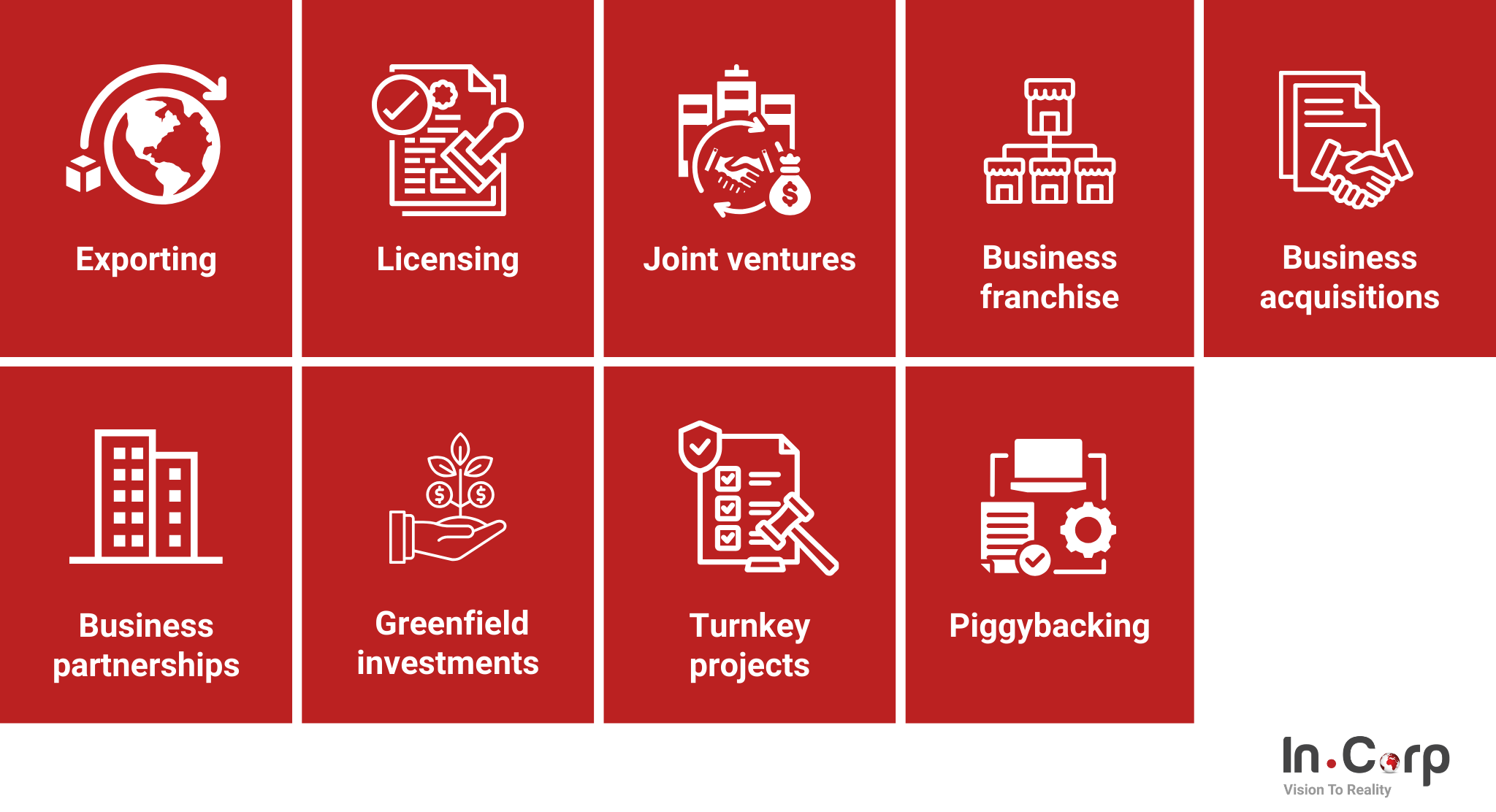
There are 9 market entry strategies that can facilitate your business’s expansion into new markets. Each offers unique approaches to overcome international barriers and capitalize on growth opportunities.
1. Exporting
Direct exporting involves selling products directly to foreign customers, often through local distributors or agents. This approach allows for greater control over marketing and sales, ensuring consistent brand representation and product quality worldwide.
2. Licensing
Licensing grants local businesses the right to use your intellectual property for a fee. While it reduces market entry costs and risks, it may limit control over brand management and product quality.
3. Joint ventures
Collaborating with local businesses through joint ventures allows access to local expertise and resources but requires careful management of partnership dynamics to avoid conflicts.
4. Business franchise
Franchising enables rapid market expansion with reduced financial risk, as franchisees invest in and operate local outlets under your brand, adhering to established standards and procedures.
5. Business acquisitions
Buying existing businesses in the target market provides immediate market presence and customer base, though integration challenges and high acquisition costs must be managed.
6. Business partnerships
Strategic alliances with local partners leverage shared resources and market knowledge, but to be effective, they require alignment in goals and operational practices.
7. Greenfield investments
Building operations from scratch in a new market offers complete control over business processes and customization to local needs, but it involves high initial costs and longer ROI timeframes.
8. Turnkey projects
Contracting local firms to build and set up facilities provides a ready-to-operate business, minimizing operational risks but relying heavily on contractor performance.
9. Piggybacking
Utilizing existing local distribution channels or resources through partnerships allows quicker market entry with lower costs yet requires dependency on partner capabilities and alignment in market strategies.
Each strategy presents unique advantages and challenges, tailored to fit different business objectives and market conditions for successful international expansion.
Engage with a market entry consultant
Market entry consultants are crucial in helping companies navigate the complexities of expanding their business internationally.
Although the challenges encountered are often similar, each case presents unique details that require the expertise of seasoned consultants to overcome effectively. Typically, the services provided include:
1. Market analysis
Foreign market analysis extends beyond traditional domestic assessments, addressing uncertainties and nuances specific to international markets.
A knowledgeable market entry consultant offers competitive analysis, precision, and insights for accurate decision-making.
2. Analysis of international readiness
Successful international expansion begins with assessing a company’s readiness across organizational, financial, and talent dimensions before exploring foreign market opportunities. This preparatory step is essential to mitigate risks associated with global business ventures.
3. Feasibility study
A feasibility study conducted by experienced consultants evaluates the viability of entering new foreign markets. It outlines alternative approaches and identifies fundamental requirements, clarifying the needs of companies exploring internationalization.
4. Market entry strategy
A market entry strategy demands meticulous planning to minimize delays and costs. Given the dynamic nature of international markets, an experienced consultant is indispensable in designing and overseeing the implementation of an effective strategy.
5. Cross-cultural training and talent acquisition
Cultural differences often pose significant challenges in international business ventures. Consultants with local market knowledge facilitate cross-cultural training and assist in acquiring local talent, ensuring smooth operations and better integration into target markets.
These consultancy services are essential for companies expanding their successful domestic operations into global market entry.
They provide strategic guidance and operational support tailored to international business requirements.
Let InCorp handle your market entry
A well-defined market entry strategy is crucial for businesses aiming to penetrate new markets successfully.
However, executing this strategy can be challenging due to unfamiliar regulations, cultural differences, and market dynamics.
InCorp offers comprehensive support to ease this process for businesses looking to establish themselves in Indonesia.
- Company registration: Efficiently establish your legal entity with our company registration services.
- Business licensing: Obtain necessary permits and licenses to operate smoothly.
Entering a new market can be intricate and time-consuming. Click the button below to streamline your journey with our comprehensive market entry support in Indonesia.
Get in touch with us.
What you'll get
A prompt response to your inquiry
Knowledge for doing business from local experts
Ongoing support for your business
Disclaimer
The information is provided by PT. Cekindo Business International (“InCorp Indonesia/ we”) for general purpose only and we make no representations or warranties of any kind.
We do not act as an authorized government or non-government provider for official documents and services, which is issued by the Government of the Republic of Indonesia or its appointed officials. We do not promote any official government document or services of the Government of the Republic of Indonesia, including but not limited to, business identifiers, health and welfare assistance programs and benefits, unclaimed tax rebate, electronic travel visa and authorization, passports in this website.



