Pre-tax litigation is a proactive approach to resolve tax disputes before they escalate to formal legal proceedings. It allows taxpayers to address disagreements with the Directorate General of Taxes (DGT) through administrative negotiation, saving time and resources.
This article explores the key aspects of pre-tax litigation in Indonesia, from the types of disputes it covers to the essential key steps.
What is pre-tax litigation?
Pre-tax litigation is an administrative process that resolves tax disputes, such as tax assessments, penalties, or compliance, between taxpayers and tax authorities before formal litigation. It involves negotiation, objection filing, and mediation, helping taxpayers avoid the costly and lengthy procedure of formal litigation.
Taxpayers can engage in this tax procedures with the Directorate General of Taxes (DGT) to clarify misunderstandings, correct errors, and potentially reduce penalties or tax liabilities. This approach promotes cooperation and ensures disputes are resolved efficiently.
Types of tax disputes that can proceed to pre-tax litigation
Tax disputes can arise from various issues, often involving disagreements between taxpayers and the Directorate General of Taxes (DGT). Many disputes can be resolved through pre-litigation processes, avoiding court intervention, including:
Tax Assessment Disputes
These disputes occur when taxpayers disagree with the tax amount assessed by the DGT due to tax calculation errors, misinterpretation of laws, or conflicting views on taxable income.
Tax Penalty Disputes
These disputes relate to late filing, underpayment, or non-compliance. Taxpayers may challenge these penalties if they believe they were applied inaccurately.
Transfer Pricing Disputes
Multinational corporations often face transfer pricing disputes, where the DGT challenges the pricing of transactions between related entities to ensure balanced taxation.
Tax Exemption or Incentive Disputes
These disputes involve disagreements over applying tax exemptions or incentives, such as tax holidays or deductions.
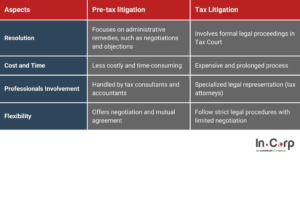
Pre-tax litigation vs. litigation services: Key Differences
Understanding the differences between pre-litigation and litigation services is crucial for taxpayers seeking to resolve disputes efficiently. Below are the key differences:
Benefits of pre-tax litigation procedures
Pre-tax litigation offers numerous advantages for taxpayers planning to negotiate their disputes before proceeding to formal court, such as:
- Cost Efficiency: Eliminates court fees and reduces legal expenses.
- Time Savings: Resolves disputes faster than litigation by reducing lengthy court schedules.
- Resolution Flexibility: Allows for tailored solutions through collaborative discussions, avoiding rigid legal outcomes
- Reduced Risk of Escalation: Resolving disputes early minimizes the likelihood of prolonged and uncertain litigation.
Read more: How to claim your tax refund in Indonesia
Pre-tax litigation procedures in Indonesia
Below is the breakdown of the pre-tax legal disputes key procedures in Indonesia, including:
1. Tax Audit and Assessment
DGT will review the taxpayer’s records to ensure compliance with tax regulations. If underpayments are identified, the DGT issues a Tax Assessment Letter or Surat Ketetapan Pajak (SKP).
2. Objection Filling
Taxpayers who disagree with the assessment can file an objection with the DGT within three months of receiving the SKP. The objection should include supporting documentation and a detailed explanation of the taxpayer’s position.
3. DGT Review and Decision
The DGT reviews the objection and issues a Decision Letter on Objection (Surat Keputusan Keberatan), including uphold, partially approve, or reject the taxpayer’s objection.
4. Consultation and Mediation
Taxpayers can negotiate tax disputes with the DGT through discussions, mediation, or alternative dispute resolution (ADR) until mutual agreement is achieved.
5. Appeals (If Necessary)
If the objection decision is unfavorable, taxpayers can file an appeal with the Tax Court. This process will end the pre-litigation process, transitioning the disputes into the litigation phase.
Read more: Understanding the duties of the Directorate General of Taxes in Indonesia
Resolve your tax disputes efficiently with InCorp
By addressing disputes early and effectively, pre-tax litigation can save you time, money, and unnecessary stress. However, navigating the procedures can be daunting and requires in-depth understanding to resolve your tax disputes seamlessly.
At InCorp Indonesia (an Ascentium Company), our expert tax advisory services are designed to guide you through the complexities of resolving your disputes. Our services included:
- Pre-tax litigation: Helping you seamlessly resolve disputes through negotiation and mediation before formal litigation.
- Financial Audit & Review: Reviewing your financial records and tax filings to ensure compliance and prepare for audits.
- SP2DK and Tax Filling: Assisting with SP2DK (Tax Collection Letters) and ensuring accurate, timely tax filing to avoid penalties.
Fill out the form below to learn how we can help you achieve the best outcomes for your tax matters.
Get in touch with us.
What you'll get
A prompt response to your inquiry
Knowledge for doing business from local experts
Ongoing support for your business
Disclaimer
The information is provided by PT. Cekindo Business International (“InCorp Indonesia/ we”) for general purpose only and we make no representations or warranties of any kind.
We do not act as an authorized government or non-government provider for official documents and services, which is issued by the Government of the Republic of Indonesia or its appointed officials. We do not promote any official government document or services of the Government of the Republic of Indonesia, including but not limited to, business identifiers, health and welfare assistance programs and benefits, unclaimed tax rebate, electronic travel visa and authorization, passports in this website.