Designed to attract local and international investors, Special Economic Zones (SEZs) provide a unique platform for fostering economic growth and innovation. This article will delve into the dynamic landscape of SEZs, examining the diverse sectors and joint ventures that define the investment climate.
Why Indonesia’s SEZs?
Indonesia’s Special Economic Zones (SEZs) play a crucial role in boosting the country’s economy. By June 2023, investments in SEZs reached IDR 128.5 trillion (USD 8.5 billion), creating 71,349 new jobs through 291 businesses.
To support the success of SEZs, the government offers various incentives, such as tax breaks, customs services, and land access. It is also expanding beyond Java to promote equal growth.
Read more: Positive Investment List improves investment in Indonesia
What are the benefits of SEZs in Indonesia?
There are several benefits to operating within SEZs, both in fiscal and non-fiscal incentives, as highlighted below:
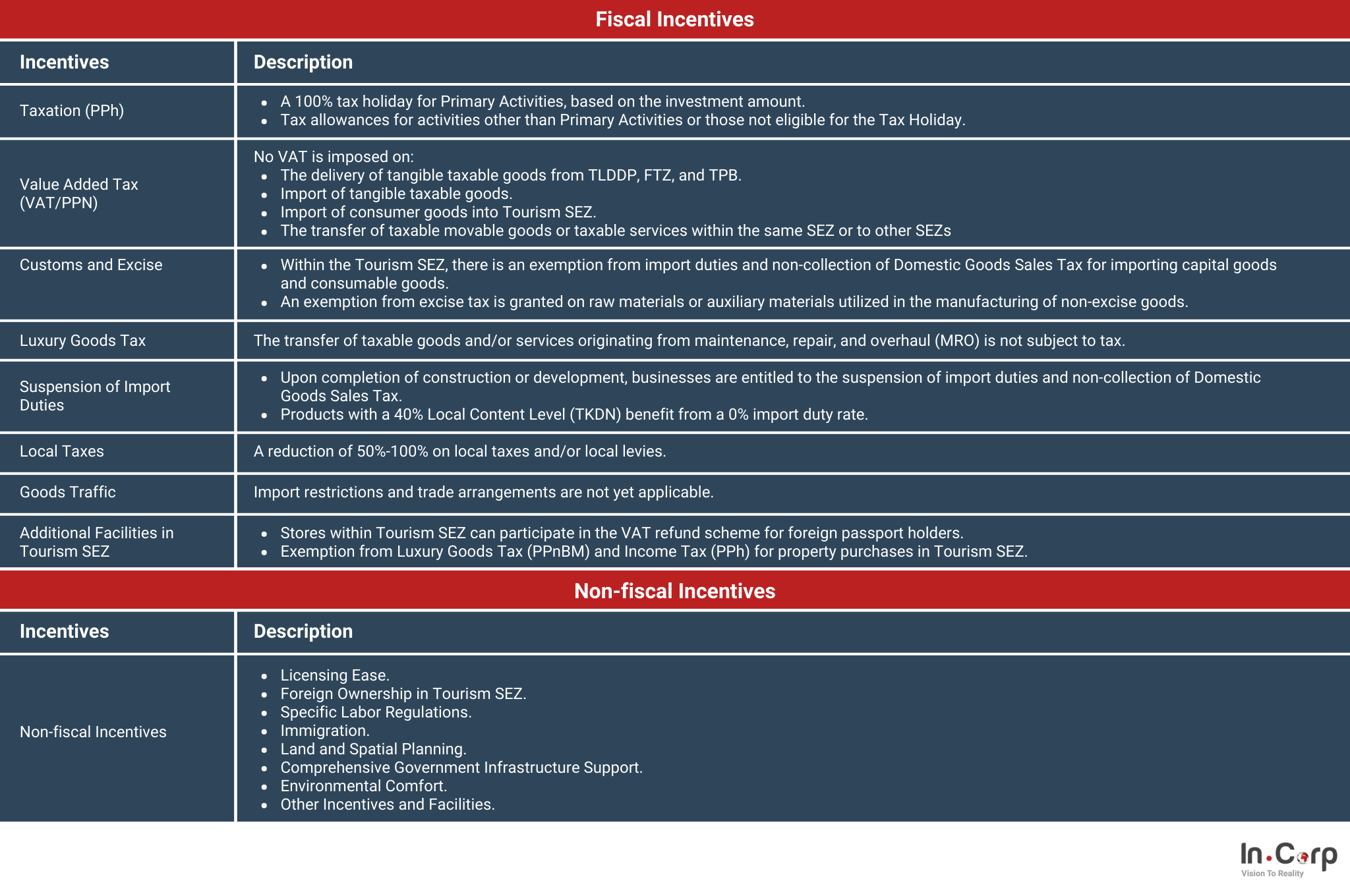
The requirements for qualifying for the SEZ benefits
Potential investors looking to conduct business activities in a SEZ and receive its facilities and benefits must meet various requirements. The government sets general requirements that can be seen as the characteristics of SEZ investors.
These investors must be domestic corporate taxpayers at the central and branch levels, conducting business activities in the SEZ and possessing business licenses.
The first aspect to consider is obtaining permits for foreign direct investment (FDI) or domestic direct investment (DDI) to obtain the ultimate facilities available in SEZs.
Investors must utilize the SEZ application system integrated with the Information and Technology (IT) inventory. This system should meet standardization and data exchange requirements with the Indonesian National Single Window (INSW) system and the customs and tax computer service system.
Investment options within SEZs
Three business models give investors options to inject their funds within SEZs:
Investment opportunities as a tenant or investor
- Investing in primary and supporting activities, such as industries like palm oil, rubber, petrochemicals, agriculture, fisheries, manufacturing, logistics, and tourism.
- Collaborating with developers who act as investors in joint ventures.
Investment opportunities as a developer
- Collaborating (joint venture) with a developer to build and manage SEZs.
Investment opportunities as an infrastructure developer
Investing in infrastructure development within SEZs:
- Within the area (roads, drainage, power generation, water treatment plants, wastewater treatment, etc.).
- Regional infrastructure (roads, ports, airports, railways, electricity, gas, water, etc.).
Read more: How Kendal Industrial Park attracts investors
How many special economic zones are there in Indonesia?
Indonesia’s SEZs are categorized into two types: industrial and tourism zones. Here is the comprehensive list.
Industrial SEZ
SEZs are expected to create solid linkages and synergies among various economic sectors, including small, medium, and large industries.
| Industrial SEZ | Description |
| Arun Lhokseumawe SEZ | Located in Aceh Province, this SEZ mainly supports the energy industry, petrochemical and other chemical industries, palm oil processing, wood processing, and logistics. |
| Sei Mengkei SEZ | Its primary activities in Simalungun Regency, North Sumatra, involve palm oil, rubber, tourism, and logistics. |
| Batam Aero Technic SEZ | Located in Batam City, Riau Islands Province, this industrial SEZ is designed for primary activities, particularly in aircraft maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO). |
| Galang Batang SEZ | This industrial SEZ is designated for primary bauxite processing and logistics activities in Bintan Regency, Riau Islands Province. |
| Kendal SEZ | Located in Kendal Regency, Central Java Province, its primary activities include:
|
| Gresik SEZ | Gresik SEZ, located in Gresik Regency, East Java Province, has primary activities in the metal, electronics, chemical, energy, and logistics industries. |
| Maloy Batuta Trans Kalimantan (MBTK) SEZ | MBTK SEZ occupies an area of 557 hectares in Kutai Timur Regency, East Kalimantan Province. Its primary activities include palm oil processing, energy industry, and logistics. |
| Palu SEZ | It is located in Palu City, Central Sulawesi Province, and is designed for primary activities such as bare metal industry and logistics. |
| Bitung SEZ | Bitung SEZ is situated in Bitung City, North Sulawesi. This industrial SEZ engages in primary activities such as coconut processing, fish processing, and logistics. |
| Sorong SEZ | The Sorong SEZ covers an area of 523 hectares. Its main activities include nickel processing, palm oil processing, forest product processing, sago plantation, and logistics. |
Tourism SEZ
SEZs are expected to become integrated tourism destinations, encompassing natural, cultural, and MICE (meetings, incentives, conferences, and events) tourism. The list is:
| Tourism SEZ | Description |
| Nongsa SEZ | This is the second SEZ located in Batam City, Riau Islands Province. This tourism and industrial SEZ is primarily designed for digital parks and tourism. |
| Tanjung Kelayang SEZ | This SEZ is situated in Belitung Regency, Bangka Belitung Province, and its main activities revolve around exploring tourist spots and providing accommodation. |
| Tanjung Lesung SEZ | Located in Pandeglang Regency, Banten Province, this tourism SEZ covers an area of 1,500 hectares. |
| Lido SEZ | Lido SEZ is in Bogor Regency, West Java Province. The main activities in this tourism and creative industry SEZ are tourism-related. |
| Singhasari SEZ | It is situated in Malang Regency, East Java Province, and primarily focuses on tourism and technology development. |
| Mandalika SEZ | This area, located in Central Lombok Regency, West Nusa Tenggara Province, has been operational since October 2017. |
| Likupang SEZ | Designed as a tourism SEZ, Likupang is in North Minahasa Regency, North Sulawesi Province. |
| Morotai SEZ | Morotai, designed as a tourism SEZ, is in Morotai Island Regency, North Maluku Province. Its primary activities include tourism, fish processing, and logistics. |
Challenges and factors to consider for businesses in SEZs
Several factors businesses should consider before investing in SEZs:
1. Regulatory landscape
Familiarize yourself with Indonesian SEZ regulations, encompassing investment prerequisites, taxation, and labor legislation.
2. Infrastructure availability
Examine the SEZs’ essential infrastructure like transportation, power, and water supply.
3. Market viability
Assess the potential market demand for your products or services within the SEZs and their surrounding areas.
4. Labor expenses
Research labor costs in the SEZs and the accessibility of skilled workers.
5. Political stability
Consider Indonesia’s political stability and the regional political climate near the SEZ, including potential investment risks.
6. Competitive environment
Analyze competition within the SEZs and the adjacent areas to grasp market dynamics.
7. Legal safeguards
Investigate legal protection for foreign investors in Indonesia and SEZs.
8. Local administration support
Gauge local administrations’ support and incentives to SEZ investors.
Start investing in Indonesia’s SEZs
The development of SEZs across Indonesia provides ample opportunities for businesses. If you plan to invest in these zones, partnering with InCorp Indonesia for company registration and Investor KITAS services can streamline your business setup.
Get in touch with us.
What you'll get
A prompt response to your inquiry
Knowledge for doing business from local experts
Ongoing support for your business
Disclaimer
The information is provided by PT. Cekindo Business International (“InCorp Indonesia/ we”) for general purpose only and we make no representations or warranties of any kind.
We do not act as an authorized government or non-government provider for official documents and services, which is issued by the Government of the Republic of Indonesia or its appointed officials. We do not promote any official government document or services of the Government of the Republic of Indonesia, including but not limited to, business identifiers, health and welfare assistance programs and benefits, unclaimed tax rebate, electronic travel visa and authorization, passports in this website.



