Indonesia’s strategic location in Southeast Asia presents a treasure trove of opportunities for import-export ventures. However, with many possibilities, choosing the right product can feel overwhelming. This guide will explore Indonesia’s most promising import-export business ideas.
Understanding import and export in Indonesia
Before we delve into import-export business ideas, we must first understand what import and export are.
Imports are goods and services purchased from abroad, resulting in an outflow of funds. While countries aim to export more than they import to enhance domestic revenue, a high level of imports, particularly productive assets like machinery, can signify economic growth.
Conversely, exports involve domestic goods and services sold to foreign buyers, bringing funds into the exporting country.
Types of import-export business
Import-export businesses enable international trade by facilitating the exchange of goods across borders. There are three main types, as listed below:
Import-export merchants
These independent agents purchase goods directly from domestic or foreign manufacturers and resell them profitably.
Export Trading Company (ETC)
ETCs identify market trends and connect foreign buyers with domestic manufacturers seeking to export their products. They may temporarily own the goods during transit and earn a commission upon distribution.
Export Management Company (EMC)
EMCs represent sellers specializing in specific products or industries. For instance, a furniture maker might hire an EMC to find international dealers and handle logistics and paperwork. EMCs earn through salaries, commissions, or retainers.
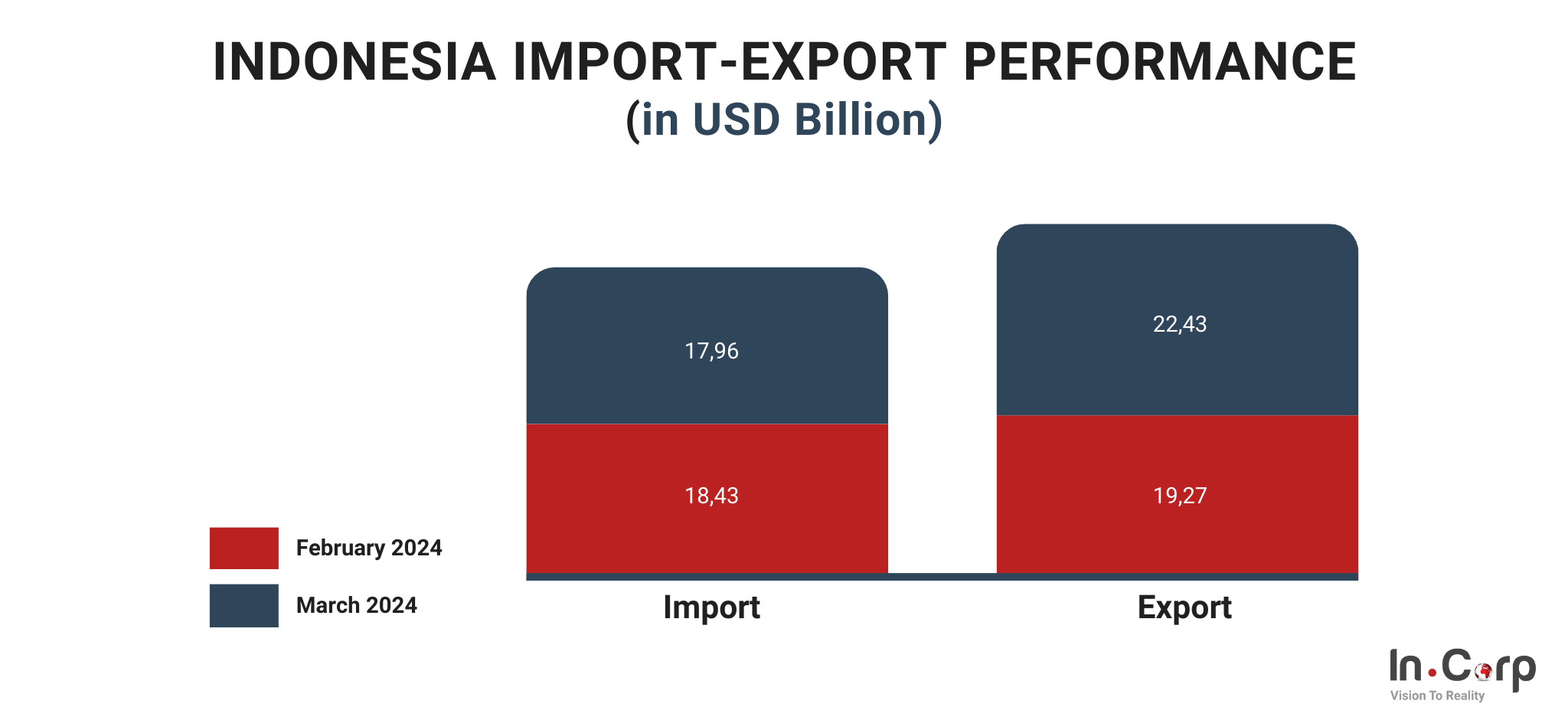
Indonesia import-export performance
In March 2024, Indonesia’s exports reached USD 22.43 billion, showing a 16.40% increase from February 2024 but a 4.19% decline from March 2023.
Non-oil and gas exports for March 2024 totaled USD 21.15 billion, reflecting a 17.12% increase from February 2024.
In March 2024, manufacturing exports decreased by 4.92%, mining and other exports fell by 17.31%, and agriculture, forestry, and fisheries exports increased by 8.05% compared to January-March 2023.
Regarding imports, Indonesia recorded USD 17.96 billion in March 2024, marking a 2.60% decrease from February 2024.
Oil and gas imports in March 2024 were USD 3.33 billion, up 11.64% from February 2024. Non-oil and gas imports totaled USD 14.63 billion in March 2024, down 5.34% from February 2024.
Read more: Navigating the landscape of Indonesian imports
Top import-export business ideas in Indonesia
If you are considering starting a business in Indonesia, here are some import-export business ideas to consider.
Import commodities
| Import | Description |
|---|---|
| Wheat Flour | Indonesia imports USD 45.29 million of wheat flour, totaling approximately 104.21 million kilograms. |
| Soybeans | Imports of soybeans amount to USD 735.437 from the United States, Argentina, Malaysia, Paraguay, and Canada. |
| Vegetables | Vegetables, primarily from China, reach a value of USD 526.8 million. |
| Mineral Fuels and Oils | Indonesia imports mineral fuels and oils worth USD 364.6 million from Iran. |
| Salt and Sulfur | Imports of salt and sulfur from Iran are valued at USD 22 million. |
| Corn | Corn imports total USD 544.189 million from India, Argentina, Brazil, Thailand, and Paraguay. |
| Fertilizers | The imports from China are valued at USD 523.8 million. |
| Iron and Steel Pipes | Imports from China are valued at USD 414.1 million, whereas iron and steel imports from Iran are worth USD 16.4 million. |
| Copper | Copper imports from China are valued at USD 376.8 million. |
| Granulated Sugar | Imports USD 31.11 million from Thailand, Malaysia, Australia, South Korea, and New Zealand. |
| Fruits | Imports from China are valued at USD 741.3 million. |
| Aluminum | Imports from China are worth USD 881.2 million. |
| Rice | Rice has a volume of 302.71 million kilograms from Vietnam, Thailand, Pakistan, India, and Myanmar. |
| Crude Oil | The imports from China are valued at USD 286.7 million. |
| Tobacco | Indonesia imports are valued at $169.2 million and weigh 38.5 million kilograms of tobacco. |
Export commodities
| Export | Description |
|---|---|
| Shrimp | Major export destinations include Japan, China, Vietnam, and Hong Kong. |
| Coffee | Major export destinations are Malaysia, Japan, and Vietnam. |
| Palm Oil | A significant export, Indonesia produced 51.3 million tons of palm oil in 2021, exported to Malaysia, China, and India. |
| Cocoa | Exports go to Malaysia, Singapore, and Japan. |
| Rubber and Rubber Products | Indonesia exports rubber products to Malaysia, Japan, and the Philippines. |
| Textile and Textile Products | The textile industry exports clothing, bedding, and bags to Singapore, Japan, and Ethiopia. |
| Footwear | Indonesian footwear, especially sports shoes, is exported to Japan, Malaysia, and the USA. |
| Electronics | Electronic products, particularly household items, are exported to Japan, Taiwan, and South Korea. |
| Automotive Components | Motor vehicle parts are exported to China, Malaysia, and India. |
| Furniture | The furniture industry exports tables, chairs, and cabinets to Japan, Australia, and the USA. |
These sectors capitalize on Indonesia’s natural resources and skilled craftsmanship and align with global demand trends, making them attractive avenues for entrepreneurs seeking import-export business ideas.
How to start an import-export business in Indonesia
Indonesia offers exciting opportunities for import-export businesses. Here’s a roadmap to navigate the process and explore lucrative import-export business ideas in the region.
Import business
1. Choose your focus and research regulations
- Decide between import and export, considering your expertise and market demand.
- Research foreign ownership limitations for your chosen industry to ensure compliance.
2. Company incorporation
- Articles of Incorporation.
- Approval from Ministry of Law and Human Rights Ratification.
- NIB (Nomor Induk Berusaha) or business identification number often functions as your import license under the OSS system.
- NPWP (Nomor Pokok Wajib Pajak) or Taxpayer identification number.
3. Additional permits and licenses (if applicable)
- Explore potential needs for permits like PSE (Electronic Processing License) or product registrations based on your specific products.
The initial phase of company incorporation takes about a week. Obtaining additional licenses can take one to six months, depending on the specific type of license and the products involved.
Export business
Several requirements must be fulfilled when establishing an export company, beginning with forming a legal entity. Options include choosing from various legal structures, such as CV, firm, PT, or cooperative.
Properly setting up your company is crucial. Before you can export from Indonesia, you need a Taxpayer Identification Number (NPWP). Additionally, you must obtain several business licenses:
- Trading Business License (SIUP) from the Ministry of Trade.
- Industrial License from the Ministry of Industry.
- Domestic Investment Business License (PMDN) or Foreign Investment (PMA) from the Ministry of Investment (BKPM).
- Export Identity Number (APE).
Guide to Doing Business in Jakarta

Launch your import-export business ideas with InCorp
The Indonesian import-export business ideas offer many opportunities, though navigating complexities requires dedication and effort. At InCorp, we can overcome these challenges and flourish in this dynamic market.
- Company registration: We handle complex company registration and NIB acquisition through the OSS system, freeing you to focus on strategy.
- Permit and license: We also help you succeed in your export and import ventures by assisting you with all necessary permits and licenses.
Click the button below to launch your import-export business ideas and thrive in Indonesia’s market.